Plants need additional nutrients to grow because the soil itself does not provide sufficient nutrition for optimal growth.
EDTA Chelate micronutrients is an essential component to improve plant growth.
We introduce our product: EUROSOIL Micronutrients.
Our products are made from EDTA combined with Chelates. By using our product, it will recondition the soil and allow optimal intake of food by the tree roots. This product is required throughout the growth cycle to support the growth process.
If the microelement is not chelated at a certain pH level, the concentration of crop shape will significantly decrease down to 40-50% for iron (Fe) and 10-20% for copper (Cu). EDTA chelate binds with microelements to keeps them in a plant-available form. Therefore, EDTA-fertilizers are effective and long-acting to provide plants with all the necessary nutrients.


Most soil, especially, plant soil does not provide the essential nutrients for optimum growth.
Why EDTA is important on fertilizers ? It has been used for over 60 years, mainly in the detergent industry and as a component in fertilizers. The scientific name of EDTA is Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid.
EDTA-fertilizers are effective and long-acting because plants are supplied with the necessary nutrients for a healthy growth.
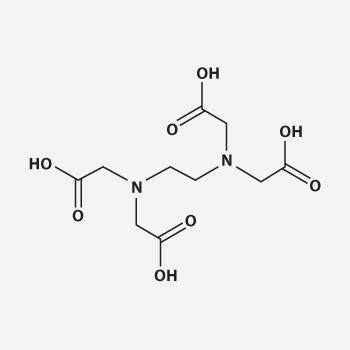
a complex of micronutrient ion and an organic molecule called ligand. As long as the ion is attached to the ligand,
it is protected from interacting with other ions in the solution
This mechanism maximizes the efficiency of the micro nutrients applied
and ensure availability of micronutrients in both alkaline and acidic soils.